CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Set 9 with Solutions
Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science with Solutions Set 9 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Set 9 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks : 80
General Instructions:
- The question paper consists of five sections (A, B, C, D and E) with 30 questions in total.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question numbers 1 – 12 are multiple choice questions of one mark each.
- Question numbers 13 – 18 are of 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 50 – 60 words each.
- Question numbers 19 – 23 are of 4 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 100 – 120 words each.
There is an internal choice in two of the 4 marks questions. - Question numbers 24 – 26 are passage, cartoon and map-based questions. Answer accordingly.
- Question numbers 27 – 30 are of 6 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 170 – 180 words.
- There is an internal choice in 6 marks questions.
Section A (12 Marks)
Question 1.
Match the following. (1)
| List I | List II |
| A. Economic and Social Council | 1. Resolves disputes between and among members countries. |
| B. International Court of Justice | 2. Debates and discusses global issues |
| C. Security Council | 3. Preservation of international peace and security. |
| D. General Assembly | 4. Looks into the economic and social welfare of the member countries. |
Codes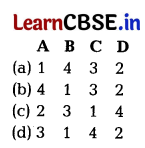
Answer:
(b) 4 1 3 2
| List I | List II |
| A. Economic and Social Council | 4. Looks into the economic and social welfare of the member countries. |
| B. International Court of Justice | 1. Resolves disputes between and among members countries. |
| C. Security Council | 3. Preservation of international peace and security. |
| D. General Assembly | 2. Debates and discusses global issues |
Question 2.
The 14th Summit of NAM was held in …………….. . (1)
(a) Brussels, 2000
(b) Havana, 2006
(c) Paris, 2005
(d) Switzerland, 2006
Answer:
(b) Havana, 2006
![]()
Question 3.
The superseding agency of Planning Commission of India is …………….. . (1)
(a) National Development Council
(b) NITI Aayog
(c) Council of Industrial and Scientific Research
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) NITI Aayog
Question 4.
Which one of the following agency of UN is related to environmental issues? (1)
(a) UNDP
(b) UNEP
(c) UNESCO
(d) UNHRC
Answer:
(b) UNEP
Question 5.
How many countries fought against Iraq during the First Gulf War? (l)
(a) 32
(b) 33
(c) 34
(d) 35
Answer:
(c) 34
Question 6.
The Planning Commission was dissolved in which year? (l)
(a) July 2014
(b) August 2014
(c) September 2014
(d) October 2014
Answer:
(b) August 2014
Question 7.
How many seats did NDAIV got in the 2019 Lok Sabha elections? (l)
(a) 303
(b) 350
(c) 320
(d) 323
Answer:
(b) 350
Question 8.
In which year the Afro Asian conference known as the Bandung Conference was held? (l)
(a) 1952
(b) 1961
(c) 1955
(d) 1954
Answer:
(c) 1955
Question 9.
When did the idea of global security emerge? (l)
(a) 1990
(b) 1992
(c) 1991
(d) 1995
Answer:
(a) 1990
Directions (Q. Nos. 10 and 11) In the questions given below there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read these statements and choose the correct option.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Question 10.
Assertion (A) : India, China and other developing countries were exempted from the requirement of the Kyoto Protocol.
Reason (R) : Their contribution to the emission of greenhouse gases during the industrialisation period was not significant. (1)
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 11.
Assertion (A) : The era of multi party system began after the election of 1989.
Reason (R) : Election in 1989 led to the defeat of the Congress party and ended its dominance over the Indian Party System. (1)
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
![]()
Question 12.
Arrange the following in a correct sequence. (1)
1. UN Sustainable Development Summit
2. UN Conference on Sustainable Development
3. General Assembly Special Session on the Environment
4. United Nations Conference on Environment and Development
Codes
(a) 2, 4, 3,1
(b) 1,2, 4, 3
(c) 4, 3, 2, 1
(d) 3, 4, 2, 1
Answer:
(c) 4, 3, 2, 1
Section B (12 Marks)
Question 13.
Who was Potti Sriramulu? What was the outcome of his indefinite fast? (1 + 1 = 2)
Answer:
Potti Sriramulu was a Congress leader and a Gandhian follower who participated in salt-satyagraha with Gandhiji. He undertook a fast unto death, demanding a separate state of Andhra Pradesh. The outcome of this indefinite fast led to his death on 15th December, 1952.
Question 14.
What is meant by non-Congressism? (2)
Answer:
The term non-Congressism was coined by Ram Manohar Lohia. He advocated that the Congress’s rule was undemocratic and opposed the interests of ordinary poor people.
Thus, all other parties came and organised themselves. This system was non-Congressism. It also reclaimed the democracy for the people.
Question 15.
What was the main reason behind the split of Congress in 1969? (2)
Answer:
The main reasons behind the split in Congress in 1969 were
- The factional rivalry between the Syndicate and Indira Gandhi.
- Abolition of Privy Purse.
Question 16.
State any two objectives of the UN. (1 + 1 = 2)
Answer:
The two objectives of the UN are
- To maintain international peace and security
- To facilitate co-operation among member countries by avoiding conflicts and war
Question 17.
Name any two functions of the General Assembly of the UN. (1 + 1 = 2)
Answer:
Two functions of the General Assembly of the UN are
- To discuss and make recommendation on any issue under the ambit of the UN Charter
- To maintain international peace and security
Question 18.
Why are Coalition Governments formed? Explain. (2)
Answer:
Coalition Governments usually are a temporary alliance, being formed when no single political party gains a clear majority and competing parties instead negotiate to work together. It acts as a channel to meet the expectations and redress the grievances of different groups.
![]()
Section C (20 Marks)
Question 19.
What are the non-traditional notions to security? (4)
Answer:
Non-traditional notions to security includes a wide range of threats affecting the conditions of human existence. It focuses on human security and global security which are discussed below
(i) Human Security : It refers to protection of people more than the protection of states.
Here, state does not mean secure people. For example, more people have been killed by their own governments rather than by the foreign armies in the last 100 years.
(ii) Global Security : The idea of global security came up in the 1990’s in response to the global nature of threats like global warming, international terrorism and health epidemics like AIDS and bird flu, etc.
Therefore, it cannot be resolved by a single country rather a comprehensive effort of all countries is required to deal with such issues.
Question 20.
Which steps must be adopted to conserve the natural resources? (4)
Answer:
Following steps must be adopted to conserve the natural resources
- Afforestation, preventing the felling of immature and young trees and creating awareness amongst the local people about planting and nurturing trees may help in conserving forests.
- Terrace farming in hilly regions, contour ploughing, controlling the shifting cultivation, overgrazing and plugging the gullies. Some of are the import methods of soil conservation.
- Construction of dams to impound rain water, use of sprinklers, drip or trickle irrigation technique, recycling of water for industrial and domestic purposes will help in conservation of the invaluable water resource.
- Minerals are non-renewable resources need to be conserved through efficient utilisation, development of better technology of extraction and purification, recycling of minerals and use of substitutes.
Question 21.
Explain any four effects of globalisation on the economy of a country. (4)
Answer:
Following are the four effects of globalisation on the economy of a country
- Economic globalisation gives more importance to institutions like the IMF and the WTO.
- It involves greater economic flows among different countries of the world.
- As the restrictions imposed by different countries have been reduced, so greater trade in commodities across the globe can be seen.
- It has led to the flow of ideas across national boundaries through internet and computer.
Question 22.
Explain any four features of the Communist Party of India. (1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4)
Or
What were the significant impacts of the fourth general elections in India in 1967 on the dynamics of Indian politics?
Answer:
The four features of the Communist Party of India (CPI) are
- The Communist Party of India is inspired by the Bolshevik Revolution in Russia and advocated socialism as the solution to problems affecting the country.
- Soon after Independence, the party thought that the transfer of power in 1947 was not true independence and encouraged violent uprising in Telangana.
- The basic question that troubled the party was the nature of Indian Independence.
- In 1951, the Communist Party abandoned the path of violent revolution and decided to participate in the approaching general elections.
Or
The fourth general election held in 1967 was the first election to be held without Nehru. Congress was dominant party before 1967, but scenario was likely to change after 1967’s election. Several non-Congress parties joined to form a big alliance called Samyukt Vidhayak Dal. Congress still managed to win in Lok Sabha election, but with the poorest performance ever, Congress lost in many states.
Many Congress leaders left the party in order to join the other party. Local politics gained momentum. In Tamil Nadu, a non-Congress party won on its own for the first time. The opposition parties got together and formed anti-Congress fronts in some states.
This strategy was given the name of non-Congressism by Ram Manohar Lohia. He argued that Congress rule was undemocratic and opposed the interests of ordinary people. Therefore, the non-Congress parties were necessary for reclaiming democracy for the people.
Question 23.
Discuss the relations between India and Israel. (4)
Or
Explain how the foreign policy of a nation is influence by its political leadership. Support your explanation with examples from India’s foreign policy?
Answer:
The relations between India and Israel are discussed below
- The diplomatic relations formally developed between the two after the opening of Israeli embassy in India in 1992. Since then the bilateral relationship between the two countries has prospered at the economic, military, agricultural and political levels.
- The relations between two countries started gaining firmness only after the formation of BJP-led NDA Governments in 1996 and 1998 onwards. India has become one of Israel’s largest trading partners.
- Later on relations between the two democratic countries further intensified with the visits of the two heads of the government i.e. Prime Minister Narendra Modi to Israel in 2017 and Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu to India in 2018.
- The two nations have started cooperation in various fields like cultural exchange, space research, security and defence, counter terrorism, water, energy and agricultural development.
Or
Political leadership of a nation always affect its foreign policy. There are two examples given below
(i) Foreign Policy of Nehru : Nehru was the main architect of foreign policy after independence.
He had a deep knowledge of world affairs.
He was the main leader to advocate the unity of the Asian nations. The main elements of his foreign policy were as follows
- Non-Alignment Movement
- Panchsheel Agreement
- Not to join any of the two blocs (US and USSR).
- To promote the international peace and co-operation
- Nuclear disarmament and promoting democratic relationship with overseas
(ii) Foreign Policy of Shastri, Indira Gandhi and Morarji Desai : India faced war during the period of Shastri and Mrs Gandhi. Both maintained the integrity and sovereignty of the country.
The foreign policy of both was focusing on the peace and prosperous development of India as well as with neighbouring states. They both were favouring the concept of Nehru’s Non-Aligned Movement and made good relations with Asian and African countries.
![]()
Section D (12 Marks)
Question 24.
Read the passage given below and answer thk questions that follow. (1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4)
The Assam movement from 1979 to 1985 is the best example of such movement against ‘outsiders’. The Assamese suspected that there were huge numbers of illegal Bengali Muslim setters from Bangladesh. They felt that unless these foreign nationals are detected and deported, they would reduce the indigenous Assamese into a minority. There were other economic issues too. There was widespread poverty and unemployment in Assam despite the existence of natural resources like oil, tea and coal. It was felt that these were drained out of the state without any commensurate benefit to the people.
(i) The Assam Movement was led by the group named ………….. .
(a) All India Students Union
(b) All Assam Students Union
(c) All Assam Sabha Unit
(d) All Assam Sabha Union
Answer:
(b) All Assam Students Union
(ii) Why did the Assamese seek the detection and deportation of the outsiders?
(a) As huge number of Bengali Muslims was a cause of concern for Assamese.
(b) They felt that these foreign nationals would reduce the indigenous Assamese to minority.
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(iii) What were the economic issues taken up as a part of the movement?
(a) Widespread poverty
(b) Unemployment
(c) Inflation
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
(iv) Assam movement expresses ………………. .
(a) regional aspirations
(b) migration issues
(c) regional problems
(d) violent acts
Answer:
(a) regional aspirations
Question 25.
In the given political outline map of the India, five states have been shown as A, B, C, D and E. Identify them on the basis of information given below and write their correct names in your answer book with the respective serial number of the information used and the alphabet concerned as per the following format. (1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4)
(i) The state which came into existence due to bifuraction at the time of partition in 1947.
(ii) A Princely State whose ruler resisted its merger with India.
(iii) The state where the Congress Party failed to win majority in the First General Elections of India.
(iv) The state which was created in 1966.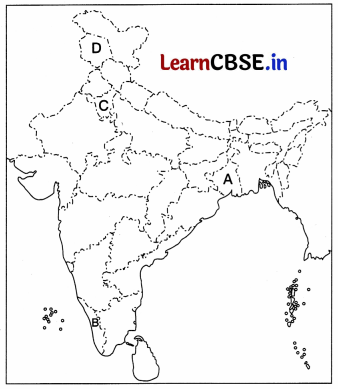
| Sr. no. of the Information Used | Alphabet Concerned | Name of States |
| (i) | ||
| (ii) | ||
| (iii) | ||
| (iv) | ||
| (v) |
Answer:
| Sr. no. of the Information Used | Alphabet Concerned | Name of States |
| 0) | A | West Bengal |
| 00 | D | Jammu and Kashmir |
| (iii) | B | Kerala |
| (iv) | C | Haryana |
Question 26.
Study the given cartoon and answer the questions that follow.
(i) Who was head of the government formed by the National Front in 1989?
Answer:
VP Singh was the head of government formed by National Front in 1989.
(ii) Why was the government formed by him called a puppet government?
Answer:
The government formed by him called a puppet government because strings of government were in the hands of other leaders
(iii) What is meant by support of government from outside?
Answer:
Support from outside means to support the functioning and process of the government without joining or becoming a part of government.
![]()
Section E (24 Marks)
Question 27.
Examine the basis of projection of China to overtake the US as the largest economy of world by 2040. (6)
Or
Compare and contrast the ‘shock therapy’, of the USSR with ‘ the open door’ policy of China.
Answer:
China is viewed to dominate US by the year 2040. The basis of the projection are . China is considered as the driver of East-Asian growth because of the economic integration into regions. China is considered to be very powerful and factors such as population, landmass, resources, regional location and political influence adds to its strength.
China announced ‘Open Door’ policy in 1978 which aimed at generation of high productivity by investments in capital and technology from abroad. In economic sector, various steps were taken to encourage investment by Western entrepreneurs for modernisation of industry, science and technology, agriculture and military. In 1980, China became the member of World Bank and International Monetary Fund.
privatisation of agriculture and industry helped in growing economy rapidly.
Foreign trade grew with the creation of SEZs and new trading laws. This resulted in high foreign exchange reserves. In this way, China became most significant for FDI.
The above points show China’s ability to overtake US as world’s largest economy by 2040.
Or
Shock Therapy of USSR
The model of transition (tansfer) from capitalist economy to free trade private economy in Russia, Central Asia and East Europe came to be know as ‘Shock Therapy’. It was influenced by World Bank and IMF. These countries removed the structures that were evolved during the Soviet period. The private ownership of property. In these countries, privatisation of state assests and corporate ownership pattern were implemented and the – collective farms were replaced by private farming and capitalism in agriculture.
Free trade was considered necessary, so free trade regime and Foreign Direct Investment, (FDI) were the main engines of change which included openness to foreign foreign investment, financial opening up or deregulation and currency convertibility.
Open Door Policy of China
The Chinese leadership took major policy decisions in the 197Gs. Like the end of its political and economic isolation with the establishment of relations with United States in 1972. These decisions led to the foundation of China’s development. The Chinese opened its economy very gradually and did not opted for the Shock Therapy. The privatisation of agriculture and industry. Trade barriers were eliminated. All these inclusive economic steps were known as Open Door Policy of China.
Question 28.
Examine the common issues of South Asian countries. (6)
Or
Elucidate the ethnic conflict in Sri Lanka and mention any two consequences of it.
Answer:
South Asia includes countries like India, Pakistan, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Maldives and Sri Lanka. The various natural areas such as Himalayas, Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean are part to this region.
The common problems among them are
- Poverty : All countries of South Asia suffered from large masses living in poverty. In India, nearly 22 per cent people are living under poverty as per 2011-12 Census.
- Violation of Human Rights : There exists a great threat to human rights from anti-social elements, communalists and from people with negative attitude, thinking and approach.
- Problem Faced by Democracy : Several countries of South Asia aspire to be a democratic country, but face a problem of stable democracy.
- Women Empowerment : Women are generally seen at lower position in most of the South Asian nations. They are restricted and are not as free as their counterparts.
Or
The democratic setup of Sri Lanka was disturbed by the ethnic conflict among the Sinhalese and Tamil origin people.
The bone of contention was the region of Ceylon which was represented by the majority Sinhala group. They opposed the migration and settlements of Tamilians from India in their region. According to the group, Sri Lanka was only for Sinhala people and not for Tamils. This attitude of Sinhala people led to the establishment of Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE), a militant organisation, which desired for a separate country.
The consequences of ethnic conflict led to the following situations
(i) There was a pressure on the Government of India by the Tamils of Indian origin to intervene in the matter. Hence, the Government of India tried to negotiate with the Government of Sri Lanka on Tamil’s question. But direct involvement was in the year 1987. India conceded to sent troops to Sri Lanka for the preservation of relations between Tamils and Sri Lankan Government. Eventually, the Indian troops got into a fight with LTTE.
(ii) The presence of Indian troops was not liked by many Sri Lankans and hence in 1989, the Indian Peace Keeping Force (IPKF) pulled out of Sri Lanka without attaining its objective.
Question 29.
Mention any three positive and three negative of Soviet system in the Soviet Union. (6)
Or
Why did Soviet Union disintegrate. Give any six reasons behind it.
Answer:
The three positive features of the Soviet system were
- The Soviet economy was more developed than the rest of the world except the US. It had a complex communication network, vast energy resources, machinery production and a transport system that connected its remotest areas.
- A minimum standard of living for all citizens was ensured by the Soviet state and the government subsidised basic necessities including health, education, child care and other Welfare schemes.
- State ownership was given more importance. Land and productive assets were owned and controlled by the Soviet state.
The three negative features of the Soviet system were
- The Soviet system was very bureaucratised and authoritarian in nature. It turned the life of the people into disorder. Authoritarianism meant the absence of democracy and freedom of speech which angered the people.
- Soviet economy witnessed economic stagnation for a long time which led to the market failure, when demand failed to meet supply in the market for consumer goods.
- State treasury had spent a huge fortune on building and maintaining nuclear arsenals and in developing its satellite states in East Europe and within the Soviet system. It turned into a large economic burden for the Soviet system.
Or
Some of the reasons which are mainly responsible for the disintegration of Soviet Union are discussed below
- Internal weaknesses of Soviet political and economic institutions failed to meet the aspirations of the people.
- The economy of the Soviet Union became stagnant which led to severe consumer shortages and disbelief and doubt in the system.
- The Soviet economy used much of its resources in maintaining a nuclear and military arsenal and the development of its satellite states in Eastern Europe and within the Soviet System, which led to huge economic burden.
- Ordinary citizens also became aware about the economic advancement of the West and disparities between their system and the systems of West.
- The Soviet Union too became stagnant due to rampant corruption, the unwillingness to allow more openness in government and the centralisation of authority in a vast land. People were alienated by slow and stifling administration that was no more accountable to the people.
- The party bureaucrats gained more privileges then ordinary citizens. People did not associate with the system and with the rulers and the government lost citizens’ support.
![]()
Question 30.
Explain the process of Partition of India in 1947. (3 + 3 = 6)
Or
It is said that the nation is to a large extent an ‘imagined community’ held together by common beliefs, history, political aspirations and imaginations. Identify the features that make India a nation.
Answer:
The process of Partition of India in 1947 is explained below
It was decided that India would be divided into two countries i.e. India and Pakistan. Such a division was not only very painful, but also very difficult to decide and to implement. It was decided to follow the principle of religious majorities. This basically means that areas where the Muslims were in majority would take up the territory of Pakistan. The rest was to stay with India.
The idea might appear simple, but it presented all kinds of difficulties. Firstly, there was no single belt of Muslim majority areas in British India. There were two areas of concentration one in the East and one in the West. There was no way that these parts could be joined. So, it was decided that the new country. Pakistan will comprise of two territories i.e, West and East Pakistan separated by a long expanse of Indian Territory.
Secondly, not all Muslim areas wanted to be in Pakistan Khan Abdul Gaffar Khan, the undisputed leader of the North Western Province and known as Frontier Gandhi, was staunchly opposed to the two-nation theory. Eventually, his voice was simply ignored and the NWFP was made to merge with Pakistan.
The third problem was that two of the Muslim majority provinces of British India, Punjab and Bengal had very large areas where the non-Muslims were in majority. Eventually it was decided that these two provinces would be bifurcated according to the religious majority at the district or even lower level.
This decision could not be made by the midnight of 14th-15th August it meant that a large number of people did not know on the day of independence whether they were in India or in Pakistan. The partition of these two provinces caused the deepest trauma of partition.
This was related to the fourth and the most intractable of all the problems of partition. This was the problem of minorities on both sides of the border. Lakhs of Hindus and Sikhs in the areas that were now in Pakistan and an equally large number of Muslims on the Indian side of Punjab and Bengal (and to some extent Delhi and surrounding areas) found themselves trapped.
The minorities on both sides of the border were left with no option except to leave their homes, often at a few hours notice. A nation is defined as a group of people living in a common geographical area, sharing common history, language, religion, descent, ethnicity and culture.
Features that make India a nation are as follows
India is a land of immense diversities. It is multi-lingual, multi-religious, multicultural and multi-regional country. With all sorts of diversities, the country has maintained unity and integrity. There is unity amidst diversity. Despite all the crisis, political decay, chaos, instability changes and challenges, the country has remained its unity, integrity and nationhood.
India as a nation is held together with same political aspirations which ensures democratic set-up based on Parliamentary form of government that inculcates political competition in a democratic framework.
Indian society is based on welfare state i.e. on the principles of equality, freedom, protection to socially disadvantaged groups and religions, etc, There will be no discrimination on the basis of religion, race, sex or place of birth as per the Indian Constitution.
