CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics Set 9 with Solutions
Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics with Solutions Set 9 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics Set 9 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains two sections
Section A- Macroeconomics
Section B- Indian Economic Development - This paper contains 20 Multiple Choice Questions of 1 Mark each.
- This paper contains 4 Short Answer Questions of 3 Marks each to be answered in 60 to 80 words.
- This paper contains 6 Short Answer Questions of 4 Marks each to be answered in 80 to 100 words.
- This paper contains 4 Long Answer Questions of 6 Marks each to be answered in 100 to 150 words.
Section A
(Macroeconomics)
Question 1.
If bank wants to increase credit creation, then …….. . (1)
(a) they should reduce the interest rate
(b) they should increase lending
(c) they should decrease lending
(d) they should increase interest rates
Answer:
(d) they should increase interest rates
Question 2.
“Suppose there has been an increased demand of Japanese Yen in July 2022, which has resulted in its appreciation and depreciation of Indian rupee.” What could be the possible reason(s) for the same? (1)
(a) There has been an increased demand of Japanese goods by Indian residents
(b) Indian government decided to repay the loan taken during Covid- 19
(c) Indian tourists have considered visiting Japan during their vacations
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
![]()
Question 3.
The government can achieve its budget objective of ‘redistribution of income’ by ……… . (1)
(a) managing the general price level in the economy to the desired level
(b) increasing the Gross Domestic Products (GDP) of the economy
(c) bringing the production of goods and services under its direct and absolute control
(d) rationalisation of taxes in pro-poor direction
Answer:
(d) One of the major objectives of government budget is the redistribution of income by imposing higher taxes on higher income group and lower taxes from lower income group or giving subsidies to poor.
Question 4.
Which of the following government transactions are used to keep the BoP in balance and which are not carried out for profits?(1)
(i) Borrowing form IMF and other financial institutions
(ii) Grants and donations
(iii) Foreign exchange reserves
Codes
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
(c) (i) and (iii)
Question 5.
Suppose in an economy, the initial deposits of ₹ 400 crores lead to the creation of total deposits worth ₹ 4,000 crores. Under the given situation, the value of reserve requirements would be ………. .
(a) 0.01
(b) 1
(c) 0.1
(d) 0.4
Answer:
(c) Money Created = Initial Deposits × Money Multiplier Also, Money Multiplier = \(\frac{1}{\text { LRR }}\)
In the given case, money created is 10 times (4,000 / 400) the initial deposits so, the multiplier is 10 and thus, reserve requirement is 0.1(1/10).
![]()
Question 6.
Value of Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) varies from …….. to ……..
(a) negative infinity, positive infinity
(b) one, positive infinity
(c) negative infinity, one
(d) zero, one
Answer:
(d) The range of Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) varies from 0 to 1 i.e., minimum value being zero and maximum value being one.
Question 7.
Statement I Real and money flows are the essence of modern economic activity.
Statement II Factor services flow from household to the producers without which production activity is not possible. Likewise, factor incomes flow from producers to the households without which consumption activity is not possible.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is true and Statement II is false
(b) Statement I is false and Statement II is true
(c) Both the statements are true
(d) Both the statements are false
Answer:
(c) Both the statements are true
Question 8.
Observe the image given below carefully and identify the objective that government should pursue to deal with this situation. (1)
(a) Increase in economic growth
(b) Reducing inequality of income and wealth
(c) Reallocation of resources
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Reducing inequality of income and wealth
Question 9.
Which items in balance of payments are also called ‘above the line’ items? (1)
(a) Autonomous items
(b) Accommodating items
(c) Visible items
(d) Invisible items
Answer:
(a) Autonomous items are the international economic transactions which are made independent of the state of BoP, with a view to earn profit.
![]()
Question 10.
Find the missing figures and choose the correct alternatives. (1)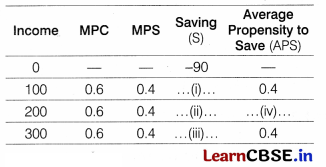
Alternatives
(a) 40,60,80,0.4
(b) 40,80,120,0.4
(c) 60,80,120,0.4
(d) 80,100,120,0.6
Answer:
(b) APS = \(\frac{S}{Y}\)
(i) 0.4 = \(\frac{5}{100}\) ; S = 40
(ii) Saving = MPS (income): Saving = 0.4 (200) Saving = 80
(iii) APS = \(\frac{S}{Y}\) ; 0.4 = \(\frac{S}{300}\) ; S = 120
(iv) APS = \(\frac{S}{Y}\) ; APS = \(\frac{80}{200}\) ; APS = 0.4
Question 11.
From the following data, calculate the value of domestic income (3)
| Items | ₹ (in crores) |
| Compensation of employees | 2,000 |
| Rent and interest | 800 |
| Indirect taxes | 120 |
| Corporate tax | 460 |
| Consumption of fixed capital | 100 |
| Subsidies | 20 |
| Dividend | 940 |
| Undistributed profits | 300 |
| Net factor income from abroad | 150 |
| Mixed income of self-employed | 200 |
Or
Define the problem of double counting in the computation of national income. State any two approaches to correct the problem of double counting.
Answer:
Domestic Income (NDP FCC)
= Compensation of Employees + Rent and Interest + Corporate Tax + Dividend + Undistributed Profits + Mixed Income of Self-employed
= 2,000+800+460+940+300+200
= ₹ 4700 crore
Or
Problem of double counting means including the value of some goods and services more than once in the estimation of national income. This leads to over estimation of the value of goods and services produced.
To avoid the problem of double counting, following two methods are used.
(i) Fiscal Output Method Aocording to this method, the value of intermediate goods is not considered. Only the value of final goods and services is considered.
(ii) Value Added Method Another method to avoid the problem of double counting is to estimate the total value added at each stage of production.
![]()
Question 12.
“When the price of a foreign currency falls, the demand for that foreign currency rises”. Explain why?
Answer:
Foreign exchange rate has an inverse relationship with the demand for foreign currency. With a fall in the price of foreign exchange, value of domestic currency increases and that of foreign currency falis. It implies that foreign goods become cheaper and their domestic demand increases.
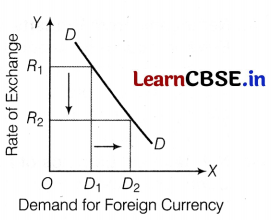
The rising domestic demand for foreign goods implies higher demand for foreign exchange which increases from O D1 to O D2, when exchange rate falls from O R1 to O R2 as shown in the figure.
Question 13.
Do you consider a commercial bank as a ‘creator of money’ in the economy?
Answer:
Yes, the primary function of commercial banks is money creation or credit creation in an economy. By the historical experience of commercial banks, they know that the depositors would not be withdrawing all of their funds at a particular time. That is why, they create credit in the form of much higher demand deposits than their cash reserves. Commercial banks issue loans on the basis of their demand deposits, even if a fraction of the amount is with them as cash reserves.
In this way, they contribute to increase the flow of money in an economy by the process of credit creation. e.g. Suppose a bank has a cash reserve of ₹ 1,500 and demand deposits of ₹ 12,000. It means the bank is creating credit of 8 times of 1 / 5 cash reserve.
If the withdrawls are 12.5% of the deposits, the bank needs to keep only 12.5% of its total deposits as cash (CRR).
Here, Demand Deposits = \(\frac{1}{\text { CRR }}\) × Cash Reserves
Demand Deposits = \(\frac{1}{12.5%}\) × 1,500 = \mathbf{q} 12,000
Now, the bank can issue loans to its customers on the basis of these demand deposits, as loans are never offered in cash, but only as demand deposits in favour of the customers. Suppose, the bank issues loan of ₹ 10,500 to its customers keeping ₹ 1,500 as cash reserve.
Now, this loan is also with the bank as demand deposit. Again, the bank keeps 12.5% of this ₹ 10,500 and can give ₹ 9,187.5 to its customers as loan. Thus, the money goes on multiplying and creates new flow of money in the economy.
The total credit creation by this bank can be obtained by the following formula
Total Credit/Money Creation
= Initial Deposit × \(\frac{1}{\text { LRR }}\)
= 12,000 × \(\frac{1}{12.5%}\) = ₹ 96,000
Question 14.
If national income is ₹ 100 crore and consumption ₹ 90 crore, find the average propensity to save. When income rises to ₹ 120 crore and consumption expenditure to ₹ 108 crore, what will be the marginal propensity to consume and marginal propensity to save?
Answer:
Given, National income (M) = ₹ 100 crore
Consumption expenditure (C) = ₹ 90 crore
Saving (S) = Y-C = 100-90 = ₹ 10 crore
Average Propensity to Save (APS) = \(\frac{S}{Y}\) = \(\frac{10}{100}\) = 0.1
Increased income (Y) = ₹ 120 crore
Increased Consumption Expenditure (C)
= ₹ 108 crore
Increased Saving (S) = 120-108 = ₹ 12 crore
Change in Income (Δ Y) = 120-100 = ₹ 20 crore
Change in Consumption Expenditure (Δ C)
= 108-90 = ₹ 18 crore
Change in Saving (Δ S) = 12-10 = ₹ 2 crore
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
= \(\frac{\Delta C}{\Delta Y}\) = \(\frac{18}{20}\) = 0.9
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
= \(\frac{\Delta S}{\Delta Y}\) = \(\frac{2}{20}\) = 0.1
Therefore,
Average Propensity to Save (APS) = 0.1.
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) = 0.9.
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS) = 0.1
![]()
Question 15.
As per the following news published in The Economic Times on 27th January, 2022 “The fiscal deficit is keenly observed during the Budget as the size of the deficit may affect growth, price stability, cost of production and inflation. At times, a sustained high fiscal deficit can impact a country’s rating. An increase in the fiscal deficit, however, can also boost a sluggish economy.” Give the meaning of fiscal deficit and explain why is it important to keep a beady eye on the fiscal deficit. (4)
Or
“Tax rates on higher income group have been increased”.
Which objective of government budget is reflected in this statement? Explain.
Answer:
Fiscal deficit is the difference between the government’s total budget expenditure and total budget receipts excluding borrowings. (1)
Fiscal Deficit = Total Budget Expenditure – Total
Budget Receipts (excluding borrowings)
It is important to closely monitor the fiscal deficit for the following reasons
(i) The size of the deficit can impact economic growth as excessive borrowing and spending can lead to inflationary pressures and an unsustainable debt burden.
(ii) Repayment of loan together with interest further increases fiscal debt, which creates debt trap.
(iii) Additionally, sustained high deficits can negatively impact a country’s credit rating, making it more expensive to borrow in the future.
However, in certain situations, an increase in the fiscal deficit can be used as a policy tool to stimulate a sluggish economy spending and boosting demand.
Therefore, keeping a vigilant eye on the fiscal deficit helps policy makers make informed decisions to maintain fiscal discipline, manage inflation, promote economic stability and ensure long-term sustainability of the economy. (3)
Or The government budget objective that is reflected in the rise in the tax rate for higher income group is the redistribution of income. The main objective of the budgetary policy of the government is to reduce inequalities of income and wealth in the country. In order to achieve this objective, the government uses progressive taxation policy to reduce the inequalities of income and wealth in the country. Government imposed higher tax rates on higher income group and low tax rate on lower income group. People with income below a certain level are not levied any direct taxes altogether. On the other hand, the government spent these tax receipts on granting subsidies and providing other public services such as health and education, to people with lower income groups, the wealth gets redistributed and reduction in inequalities is achieved.
![]()
Question 16.
(i) Calculate
(a) Net national product at market price. (3)
(b) Gross domestic product at factor cost.
| S.NO | Items | ₹ (in crore) |
| i. | Rent and interest | 6,000 |
| ii. | Wages and salaries | 1,800 |
| iii. | Undistributed profit | 400 |
| iv. | Net indirect taxes | 100 |
| v. | Subsidies | 20 |
| vi. | Corporation tax | 120 |
| vii. | Net factor income to abroad | 70 |
| viii. | Dividends | 80 |
| ix. | Consumption of fixed capital | 50 |
| x. | Social security contribution by empioyers | 200 |
| xi. | Mixed income | 1,000 |
(ii) Are the wages and salaries received by Indians working in American embassy in India, forms a part of domestic product of India?
Or
(i) Explain the components of NFIA.
(ii) “Government incurs expenditure to popularise yoga among the masses”. Analyse its impact on gross domestic product and welfare of the people.
Answer:
(i) (a) NNPMP = Compensation of Employees + Operating Surplus + Mixed Income + NFLA + Net Indirect Taxes
= (1,800 + 200)+(6,000 + 400 + 120 + 80)
+ (1000) + (-70) + 100
(b) GDPFC = Compensation of Employees + Operating Surplus + Mixed Income + Consumption of Fixed Capital
= (1,800 + 200) + (6,000 + 400 + 120 + 80)
= ₹ 9,650 crore + (1,000) + 50
(ii) No, the wages and salaries received by Indians working in American Embassy in India are not a part of domestic product of India because American embassy is not a part of domestic territory of India. (1)
Or
(i) There are three components of NFIA
(a) Net Compensation of Employees The net compensation of employees receivable from the rest of the world is equal to the difference between compensation of employees received by resident workers who are living temporarily abroad or are employed abroad, and similar payments made to non-resident workers that are temporarily staying or are employed within the domestic territory of the country.
(b) Net Income from Property and Entrepreneurship It is equal to the difference between the income received by way of interest, rent and profits by the residents of a country and similar payments made to the rest of the world.
(c) Net Retained Earnings of Resident Companies Abroad Retained earning refers to the undistributed profits of the companies. Resident companies (companies belonging to one country and working in the domestic territory of some other country) retain a part of their profits for further investment abroad. Likewise, foreign companies and their branches retain a part of their profit.
(ii) The expenditure incurred by the government to popularise yoga among the masses will increase the government final consumption expenditure. With a rise in this component, the domestic income of the country will also rise.
So, the expenditure incurred by the government to popularise yoga will lead to an increase in the gross domestic product of the country.
This expenditure will also increase the welfare of the people, as is enumerated below
(a) As more and more people practise yoga, their health and immunity will improve. This will help in increasing their working capacity.
(b) As people’s health improve, so government’s expenditure on the curative aspect of health issues will decrease.
![]()
Question 17.
(i) “High propensity to consume is a virtue, while high propensity to save is not”. Do you agree? Why or why not?
(ii) “Taxation plays a crucial role in reducing excess demand in the economy”. Explain.
Answer:
(i) The given statement is correct that high propensity to consume is a virtue as consumptions are considered as an injection to the circular flow of income by increasing demand, as increased demand leads to increased production of goods and services, leading to increase in induced investment and hence, national income. On the other hand, savings are considered as leakages from the circular flow of income by reducing consumption demand and hence production, investment and national income also fall.
(ii) Excess demand refers to the situation when Aggregate Demand (A D) is greater than Aggregate Supply (AS) corresponding to full employment in the economy.
In a situation of excess demand, government raises the rates of all taxes. This reduces the purchasing power of people and reduces both consumption and investment expenditures.
A fall in consumption and investment expenditure reduces the level of aggregate demand and helps to check the problem of excess demand.
Section B
(Indian Economic Development)
Question 18.
“Green revolution leads to marketable surplus”. What does it refers to?
(a) Production of crops for self-consumption
(b) Production of crops for selling in market
(c) Production of crops for maintaining sufficient stock
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(b) Production of crops for selling in market
Question 19.
A small loan amount given to low-income households or groups is known as
(a) cash credit
(b) micro credit
(c) rural credit
(d) simple credit
Answer:
(b) Micro credit
Question 20.
Which of the given statements characterise the status of the Indian economy during the British rule?
(i) A vibrant economy with well-developed infrastructure
(ii) Stagnant economy with a heavy reliance on agricultural sector
(iii) A flourishing market and integration with the global economy
(iv) Prevalence of rampant poverty and unemployment
Codes
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii), (iii), and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(d) (ii) and (iv)
![]()
Question 21.
Which of the following regional economic groups are formed between India, China and Pakistan?
(i) ASEAN
(ii) G-8
(iii) SAARC
Codes
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Answer:
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Question 22.
Choose the correct combination between the following columns
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Right to Education Act | (i) Emergence of India as one of the four major growth centres by 2020 |
| B. The Tapas Majumdar Committee Report | (ii) India should make a transition to knowledge economy |
| C. D́eutsche Bank report on Global Growth Centre | (iii) Free education of all children in the age group of 6-14 years |
| D. World Bank report on India and the knowledge economy | (iv) Expenditure of around ₹ 1.37 lakh crore over 10 years (1998-99 to 2006-07) to bring all Indian children in the age group of 6-14 years under the purview of school education |
Codes
A B C D
A B C D
(a) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
(b) (iii) (i) (ii) (iv)
(c) (iii) (iv) (i) (ii)
(d) (iv) (iii) (i) (ii)
Answer:
(c) (iii) (iv) (i) (ii)
Question 23.
Statement I More female workforce is found in rural areas as compared to urban areas in India.
Statement II Self-employment is the most favourable occupation among females in India. (1)
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is true and Statement II is false
(b) Statement I is false and Statement II is true
(c) Both the statements are true
(d) Both the statements are false
Answer:
(c) Both the statements are true
![]()
Question 24.
is a women-oriented project to train the women about latest agricultural techniques in Tamil Nadu.
(a) Kudumbashre
(b) Self-help group
(c) TANWA
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) TANWA
Question 25.
China has a very less proportion of cultivable land due to ……… .
(i) topographic condition
(ii) climate condition
(iii) economic condition
Codes
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (i)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
(a) (i) and (ii)
Question 26.
As per the image given below, which of the following facilitates free trade?
(a) Liberalisation
(b) Privatisation
(c) Globalisation
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (c)
![]()
Question 27.
Assertion (A) It is imperative for Indian economy to undertake measures which help to promote the rural development.
Reason (R) Almost two-third of India’s population depends on agriculture and nearly one-third of rural India lives under the trap of poverty. (1)
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
Question 28.
“The supply-demand reversal of environmental resources account for the current environmental crisis”. Explain how? (3)
Answer:
Before the advent of industrial revolution, the rate of resource extraction was less than the rate of regeneration of these resources, i.e. demand was less than supply. But with expanding population and its growing needs, the demand for resources for both production and consumption went beyond the rate of regeneration of the resources.
This has resulted in a reversal of supply-demand relationship for environmental resources as now there is very high demand for environmental resources and services, but their supply is limited and even these limited resources are being over used and misused.
Question 29.
Defend or refute the given statement with valid explanation
‘It is necessary for firms to give on-the-job training to its employees’. (3)
Or
“NABARD plays a critical role in coordinating the rural financing system”. Comment.
Answer:
I defend the given statement. Firms give on-the-job training to enhance the productive skills of the workers so as to enable them to absorb new technologies and modern ideas.
It also helps in the development of the employee and is a source of human capital formation.
It can be given in two forms
(i) The workers may be trained in the firm itself under the assistance of seniors and experienced workers.
(ii) The workers may be sent off the firms campus for the training.
Or
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (ŃABARD) was set up in 1982 as an apex body to coordinate the activities of all institutions involved in the rurál financing system.
The main functions of NABARD are (any two)
(i) To grant long-term loans to the State Government for subscribing to the share capital of cooperative societies.
(ii) To take the responsibility of inspecting cooperative banks, Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) and primary cooperative societies.
(iii) To promote research in agriculture and rural development. (2)
![]()
Question 30.
Observe the image given below and briefly explain the functions performed by the environment around us. (4)
Answer:
The environment performs the following four dynamic functions
(i) Offer Production Resources Environment provides us with wide tangible resources like minerals, water and soil. These are the gifts of nature. These resources act as an input for converting natural resources into productive and useful things.
In other words, environment provides input for production that enhances human life qualitatively.
(ii) Sustains Life Environment provides us with vital ingredients like sun, soil, water and air that are necessary for the survival of life. Absence of these essential elements implies absence of life. It supports biodiversity.
(iii) Assimilates Waste The activities of production and consumption generate waste. This waste in the form of garbage is absorbed by the environment automatically.
(iv) Enhances Quality of Life Environment includes surroundings such as rivers, oceans, mountains and deserts. It provides scenic beauty that man-admires in life and adds to the quality of human life.
Question 31.
“Features of Indian agriculture itself explain the story of its backwardness”. Put out your views in the reference to this statement. (4)
Answer:
Indian agriculture is backward, despite the fact that it is of significant importance in the Indian economy. The main features of Indian agriculture are
(i) Agricultural output depends largely on rainfall and is affected by natural calamities like floods. droughts, storms, etc.
(ii) The historical, social and cultural background of state affects agricultural output.
(iii) Over three-fourth of land holdings are of small size. Thus, agriculture is a source of livelihood for poor farmers.
(iv) Farming is a way of life rather than a commercial activity. Thus, production is mainly for self-consumption.
(v) There is little use of machinery.
Question 32.
State whether the following statements are true/false, with valid arguments
(i) There was a dire need to introduce land reform measures in the agricultural sector on the eve of independence. (2)
(ii) The main objectives of the British through their infrastructure development policy was to serve their own colonial interests and not to provide basic amenities to the people. (2)
Or
“Globalisation has both positive and negative impacts on an economy”.
Explain some of the adverse effects of globalisation on the Indian economy?
Answer:
(i) The given statement is true. At the time of independence, the land tenure system was characterised by intermediaries called zamindars, jagirdars, etc: who merely collected rent from the actual tiller without contributing towards improvements on the farm.
This demotivated the actual tiller and resulted in low productivity in this sector. Because of this, there was an urgent need for land reform policy.
(ii) The given statement is true.
Under the British rule, basic infrastructure such as railways, ports, water-transport, postage and telegraph developed, but the objective behind the development of infrastructure was not to provide basic amenities to the people but to cater to their colonial interests. The objectives of the Britishers behind the development of infrastructure were
(a) Roads were developed for the purpose of mobilising armies and transporting raw materials to the nearest railway station or port.
(b) Railways were developed to encourage commercialisation of agriculture.
Or
Globalisation has the following adverse effects on the Indian economy
(i) As a result of globalisation, the local producers stand to lose due to their inability to compete with cheap imports.
(ii) To provide goods and services at competitive prices, producers try to save on costs by lowering the wages, ensuring long working hours and denying the workers various social benefits. This results in mounting unrest among workers.
(iii) Globalisation has also affected the workers of PSUs adversely. They have been affected by budget cuts, privatisation and retrenchment.
(iv) Globalisation has also adversely affected the small businessman.
![]()
Question 33.
(i) “It has been realised that the labour force participation rate is very low in India”. Given this statement suggest few measures to raise the labour force participation rate. (3)
(ii) “There is a possibility to develop information technology as an alternate livelihood option”. Comment and give reasons. (3)
Or
(i) “It has been realised that agricultural finance is not available in sufficient quantity at right time and at reasonable rate of interest.”
As an agriculturist, suggest any two measures to make the existing system of agricultural finance serve fully the needs of agriculture effectively.
(ii) “Most MNCs including small companies are outsourcing their services to the Indian economy”. Defend or refute the given statement with valid explanation.
Answer:
(i) I would suggest following measures to raise labour force participation rate
(a) There should be drastic reduction in birth and death rates to improve the age structure of population.
(b) There should be more and more opportunities for women to participate in economic activities.
(c) The general standard of health of the population must be raised.
(d) Employment opportunities should be increased.
(ii) Yes, it is possible to develop information technology as an alternative livelihood option, Information Technology (IT) has revolutionised many sectors in the Indian econorry.
This fact is described in the following points
(a) The role of IT is justified by the increased ability of the government to predict areas of food insecurity and vulnerability through its use.
(b) It also has a potential of employment generation in rural areas.
Thus, the initiative of private sector along with support from government has made it possible to develop this sector as a sustainable livelihood option.
Or
(i) As an agriculturist, I would offer following suggestions to improve the existing system of agricultural finance
(a) The supply of finance should be fully institutionalised and dependence on private sources for credit should be eliminated.
(b) It should be ensured that finance is used for production. Loans can be given in the form of goods like seeds, fertilisers, etc.
(ii) Most multinational corporations and even small companies, are outsourcing their services to India as our country has the following advantages
(a) Availability of Cheap Labour India is a country with a large population and thus. abundant supply of labour. Due to this reason, labour in India is available at low wage rates. This helps foreign companies in reducing cost of operation by outsourcing their business processes to India.
(b) Continuity and Risk Management Periods of high employee turnover will add uncertainty to the operations. Outsourcing will provide a level of continuity to the company while reducing the risk that a substandard level of operation would bring to the company.
(c) Reduced Overhead Overhead costs of performing a back office functions are extremely high but due to outsourcing those functions have become cheaper and convenient to use.
![]()
Question 34.
Read the following text carefully and answer the given questions on the basis of the same and common understanding India, China and Pakistan have travelled seven decades of developmental path with varied results. Till the late 1970s, all of them were maintaining the same level of low development. The last three decades have taken these countries to different levels. India, with democratic institutions, performed moderately, but a majority of its people still depend on agriculture. India has taken many initiatives to develop the infrastructure and improve the standard of living.
Scholars are of the opinion that political instability, over-dependence on remittances and foreign aid along with volatile performance of agriculture sector are the reasons for the slowdown of the Pakistan economy. Yet, last five years, many macroeconomic indicators began showing positive and moderate growth rates reflecting the economic recovery.
In China, the lack of political freedom and its implications for human rights are major concerns; yet, in the last four decades, it used the ‘market system without losing political commitment’ and succeeded in raising the level of growth alongwith alleviation of poverty.
You will also notice that unlike India and Pakistan, which are attempting to privatise their public sector enterprises, China has used the market mechanism to ‘create additional social and economic opportunities’.
By retaining collective ownership of land and allowing individuals to cultivate lands, China has ensured social security in rural areas. Public intervention in providing social infrastructure even prior to reforms has brought about positive results in human development indicators in China.
(i) China’s rapid industrial growth can be traced back to its reforms in 1978. Do you agree? Elucidate. (2)
(ii) Compare the development experience of India, with China and Pakistan with reference to gross domestic product of these countries. (4)
Answer:
(i) Yes, China’s rapid industrial growth is traced back to its reforms in 1978 , which were introduced in phases. In the initial phase, reforms were initiated in agriculture, foreign trade and investment sectors. Commune lands were divided into small plots which were allocated to individual households for use and not for the ownership. In the later phase, reforms were initiated in the industrial sector. Private sector firms and township and village enterprises, were allowed to produce goods.
Dual pricing was followed. Prices were fixed in two ways, farmers and industrial units were required to buy and sell fixed quantities of inputs and outputs on the basis of prices fixed by the government and the rest were purchased and sold at market price. Introduction of Special Economic Zone (SEZ) led to development of most backward regions of the country by starting up small, medium and large scale industries.
(ii) The following points are important in this context
(a) China has the second largest GDP (PPP) of US 22.5 trillion, whereas India’s GDP is US 9.03 trillion. Pakistan’s GDP (PPP) stands at 0.94 trillion, which is roughly 11% of India’s GDP.
(b) In both India and Pakistan, the contribution of agriculture to GDP was at 16% and 24% respectively. However, in China it is only 7%.
(c) In China, the contribution of industrial sector is high at 41%. For India and Pakistan, it is 30% and 19% respectively.
(d) During 2004-05, GDP of both China and Pakistan declined while GDP of India increased.
