CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Set 12 with Solutions
Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science with Solutions Set 12 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Set 12 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks : 80
General Instructions:
- The question paper consists of five sections (A, B, C, D and E) with 30 questions in total.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question numbers 1 – 12 are multiple choice questions of one mark each.
- Question numbers 13 – 18 are of 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 50 – 60 words each.
- Question numbers 19 – 23 are of 4 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 100 – 120 words each.
There is an internal choice in two of the 4 marks questions. - Question numbers 24 – 26 are passage, cartoon and map-based questions. Answer accordingly.
- Question numbers 27 – 30 are of 6 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 170 – 180 words.
- There is an internal choice in 6 marks questions.
Section A (12 Marks)
Question 1.
Identify the issue where the Government of India and Bangladesh have difference. (1)
(a) Disaster management
(b) Environmental issues
(c) Export of natural gas
(d) India’s act East policy
Answer:
(c) Export of natural gas
Question 2.
On which the non-traditional concept of security focus on? (1)
(a) Human Security
(b) Global Security
(c) Defence
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 3.
Ozone hole is present in which layer of atmosphere? (1)
(a) Stratosphere
(b) Mesophere
(c) Troposphere
(d) Lonosphere
Answer:
(a) Stratosphere
Question 4.
The process of integration of different countries is called (1)
(a) Privatisation
(b) Globalisation
(c) Liberalisation
(d) None of these
Answer:
(d) None of these
![]()
Question 5.
The crucial element of globalisation is ……………. . (1)
(a) flow of capital
(b) innovation in technology
(c) worldwide interconnectedness
(d) trade expansion
Answer:
(c) worldwide interconnectedness
Question 6.
Which Princely State of India was the first to announce to remain as an independent state? (1)
(a) Mysore
(b) Ajmer
(c) Gwalior
(d) Travancore
Answer:
(d) Travancore
Question 7.
The Janata Party split and the government which was led by Morarji Desai lost its majority in less than ……………….. . (1)
(a) 2 months
(b) 4 months
(c) 18 months
(d) 15 months
Answer:
(c) 18 months
Question 8.
Match the following. (1)
| List I | List II |
| A. Social Revolution | 1. Revolution in the way of thinking |
| B. Cultural Revolution | 2. Developing moral and spiritual values |
| C. Spiritual Revolution | 3. Establishing equality and brotherhood in the society |
| D. Thought Revolution | 4. Regeneration of cultural values in common man. |
Codes
Answer:
(c) 3 4 2 1
| List I | List II |
| A. Social Revolution | 3. Establishing equality and brotherhood in the society |
| B. Cultural Revolution | 4. Regeneration of cultural values in common man. |
| C. Spiritual Revolution | 2. Developing moral and spiritual values |
| D. Thought Revolution | 1. Revolution in the way of thinking |
Question 9.
Which among the following were not associated with Bahujan Samaj Party? (1)
(a) B P Mandal
(b) V P Singh
(c) Kanshi Ram
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Directions (Q. Nos. 10 and 11) In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Question 10.
Assertion (A) : Global atmosphere is warming up. (1)
Reason (R) : The depletion of the stratospheric ozone layer has resulted in an increase in ultravoilet radition reaching the Earth.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 11.
Assertion (A) : In the traditional view of security more threat to a country’s comes from outside its borders. (1)
Reason (R) : The international system is rather a brutal arena in which there is no central authority capable of controlling behaviour.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 12.
Arrange the following in a chronological order (1)
1. Assassination of Rajiv Gandhi
2. Formation of UPA Government
3. Mandal Recommendations
4. Formation of NDA Government
Codes
(a) 1, 2, 3, 4
(b) 3, 1, 4, 2
(c) 2, 3, 1,4
(d) 4, 1,2,3
Answer:
(b) 3, 1, 4, 2
![]()
Section B (12 Marks)
Question 13.
Which lesson was taught through the experience of 1977 – 79 elections? (2)
Answer:
The experience of 1977 – 79 taught a lesson in democratic politics is the governments that are seen to be unstable and quarrelsome are severely punished by the voters.
Question 14.
Write the objectives of National Development Council. (2)
Answer:
The objectives of National Development Council are
- To promote common economic policies in all vital spheres.
- To strengthen and mobilise the effort and resources of the nation in support of the plan.
Question 15.
Why the period was a difficult one in the domestic politics when the nuclear test was conducted in India? (2)
Answer:
The period when the nuclear test was conducted was a difficult period in domestic politics because it was followed by the Arab-lsrael War of 1973, the entire world was affected by the Oil Shock due to the massive hike in the oil prices by the Arab nations. It further led to economic turmoil in India resulting in high inflation.
Question 16.
What is meant by flows in relation to globalisation? (2)
Answer:
Flows in relation to globalisation refers to the movement of ideas, capital, commodity and people from one part to another parts of the world, which causes the process of globalisation to exist.
Question 17.
Political equations in coalition governments are unstable. How was this concept reflected in the formation of National Front Government in 1989 and United Front Government in 1996? (2)
Answer:
In 1989, the coalition government era began in India and many political parties shared the government at the Centre. This political phenomena clearly reflects political instability and uncertainty.
United Front was formed to keep out Congress from government. It was formed in 1996 with the support of BJP and Left Front. Deve Gowda was chosen Prime Minister of United Front.
Question 18.
What are the negative consequences which are affecting Chinese economy? (2)
Answer:
The four negative consequences or drawbacks in the changed Chinese economic system are
- The benefits of the reforms have not been equally received. Approximately 100 million people are still unemployed.
- Female employment and conditions of work are as bad as in Europe of the 18th and 19th centuries.
Section C (20 Marks)
Question 19.
Explain any four factors that make the European Union an influential organisation. (4)
Answer:
Four factors that make the European Union an influential organisation are as follows
- The EU is the world’s biggest economy with a GDP of more than $17 trillion in 2016, overcoming the US.
- Its currency, the Euro can pose a threat to US dollar and its share of world trade is three times larger than that US.
- The EU also has political and diplomatic influence, as two members of EU, Britain and France, hold permanent seats in the United Nation Security Council (UNSC) with several non-permanent members.
- The EU’s combined armed forces are the second largest in the world and also the second after the total spendings of US in defence.
Question 20.
Discuss the relations of cooperation and conflicts between India and Sri Lanka. (4)
Answer:
The relations of cooperation and conflicts between India and Sri Lanka are discussed below
The major issue of conflict between India and Sri Lanka is due to the ethnic conflicts in the Sri Lanka.
The Sinhalese majority has been following a policy of discrimination against the Tamils of Indian origin. The Government of India tried to negotiate with Sri Lankan government to protect the interests of Tamils, as it find it difficult to remain neutral when Tamils are politically unhappy and are being killed.
In 1987, India sent the Indian Peace Keeping Force which was not liked by the Sri Lankans. They treated this as interference in their internal affairs. Ethnic conflicts are still prevalent in some parts of Sri Lanka but India now prefers a policy of disengagement vis-a-vis Sri Lanka’s internal troubles.
India has now signed a free trade agreement with Sri Lanka. India has helped Sri Lanka in post-tsunami reconstruction.
Thus, the relations between the two countries have improved.
![]()
Question 21.
What are the objectives of military alliances? Give an example of a functioning military alliance with its specific objectives. (4)
Answer:
The objectives of military alliances are
- To form alliances with other countries to increase their effective power of the state entered in alliance relative to another country or alliance.
- These alliances are based on national interest which changes accordingly to the changing circumstances.
- Another objective of military alliance.is to maintain balance of power in a region.
For example, USA supported the Islamic militants in Afghanistan to harm USSR in 1980s, but later attacked them when Al-Qaeda launched terrorist attack against USA on 9/11.
Question 22.
Examine how the new policies and ideologies facilitated restoration of the Congress system. How far this restoration was the revival of the old Congress? (4)
Or
Describe any three major events that led to the formal split in the Congress party in 1969?
Answer:
The slogan ‘Garibi Hatao’ and the programmes followed to implement it led to two successive election victories one at the centre and other at the state level. The Congress was now in power in almost all the states. It became popular among different social sections. The Congress had become the dominant party.
However, it was not the revival of the old party. It was a different kind of party in the following ways
- It relied entirely on the popularity of the Supreme leader.
- We can say that it had somewhat weak organisational structure.
- It did not have many factors and therefore, it could not accommodate all kinds of opinions and interests.
- It depended more on the poor, the women, dalits, adivasis and the minorities.
Or
Three major events that led to the formal split in the Congress Party in 1969 were as follows
(i) The political tension inside the Congress over the unsettled question of relation between its ministerial and organisation wings became more pronounced. Indira Gandhi had acquired a certain control over the government but after the blow suffered by the Syndicate in 1967 elections, she had hardly any organisational base in the party. The veteran leader wanted that Indira should not interfere in party affairs.
(ii) After retirement of Kamaraj as party President at the end of 1967, the other members of party foiled Indira Gandhi’s attempt to have her own men elected to succeed him. But Nijalingappa was elected and none of the Indira Gandhi’s men were elected to the new working committee. She did not want to harm the unity of the party and the existence of her government by creating a conflict with the organisational wing, as the party enjoyed only a small majority in Lok Sabha.
(iii) Indira Gandhi adopted a radical ten-point programme which included social control of banks, nationalisation of 14 private banks and abolition of the privy purse or the special privileges given to former princes. The Congress divided into two factions, one was right and second was left. Left attacked on Morarji Desai as the representative of big business houses. The defeat of the Congress formalised the split in the party. The Congress President expelled the Prime Minister from the party. Indira Gandhi claimed that her group was the real Congress.
Question 23.
Assess the economic situation of India before the general elections of 1967. (4)
Or
Explain any four factors that make European Union an influential organisation?
Answer:
The economic situation of India before the general election of 1967 was worse. Failure of monsoon and drought led to serious food crises. The crises deepened due to the condition of the country which was still recovering from China war. The food crises triggered off price rise as demand for food was much more than its supply. This led to hoarding and black marketing of the essential food items.
There was massive inequalities in income and wealth. Due to this, large number of people were poor and not able to afford the basic necessities of life. This period was also marked by depletion of foreign exchange reserves, drop in industrial production and exports.
Or
The European Union has evolved over time from an economic union to an increasingly political one and has started to act more as a nation state. This can be further explained with the following points
- The EU has economic, political, diplomatic and military influence all over the world.
- The EU is the world’s second biggest economy with a GDP of more than $ 17 trillion in 2016, next to that of the US.
- It also functions as an important bloc in international economic organisations such as the world trade organisation. Two members of the EU, Britain and France, hold permanent seats on the UN security council.
- Militarily, the EU’s combined armed forces are the second largest in the world.
- In many areas, its member states have their own foreign relations and defence policies.
- EU has its own flag, anthem, founding date and common currency. The EU has tried to expand areas of cooperation while acquiring new members, especially from Soviet bloc.
![]()
Section D (12 Marks)
Question 24.
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow (1+ 1 + 1 + 1 = 4)
Way back in the late sixties, the dominance of the Congress party was challenged, but the Congress under the leadership of Indira Gandhi, managed to re-establish its predominant position in politics. The nineties and yet another challenge to the predominant position of the congress. It did not, however, mean the emergence of any other single party to fill in its place.
Thus, began an era of multi-party system. To be sure, a large number of political parties always contested elections in our country. Our Parliament always had representatives from several political parties. What happened after 1989 was the emergence of several parties in such a way that one or two parties did not get most of the votes or seats. This also meant that no single party secured a clear majority of seats in any Lok Sabha election held since 1989. This development initiated an era of coalition governments at the Centre, in which regional parties played a crucial role in forming ruling alliances.
(i) Multi-Party System refers to ………………. .
(a) a system where only one party compete for power
(b) a system where two parties compete for power
(c) A system where many parties compete for power
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) A system where many parties compete for power
(ii) Which kind of political scenario was witnessed after 1989?
(a) Era of Coalitions
(b) Era of Developments
(c) Era of Regional Parties
(d) Era of Dominance
Answer:
(a) Era of Coalitions
(iii) What is the reason behind the emergence of several parties?
(a) As no single party secured a clear majority of seats in the Lok Sabha elections.
(b) As the political scenario has changed completely.
(c) As the era of coalitions began at the Centre level of government.
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) As no single party secured a clear majority of seats in the Lok Sabha elections.
(iv) In the era of coalitions which type of parties played a crucial role in forming ruling alliances?
(a) National Parties
(b) Unrecognised Parties
(c) Regional Parties
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Regional Parties
Question 25.
In the given political outline map of Europe, four member countries of the European Union have been marked as A, B, C and D. Identify them with the help of information given below and write their correct names in your answer book along with their respective serial numbers and the alphabet concerned. (1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4)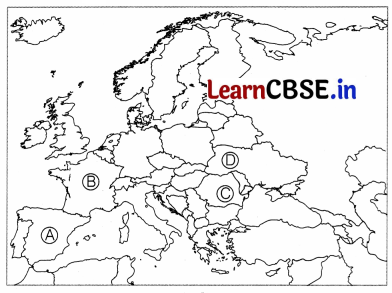
(i) An older member of the European Union located between Portugal and France.
Answer:
Spain (A)
(ii) An older member of the European Union located near Netherlands and France.
Answer:
(ii) Luxembourg (B)
(iii) A new members of the European Union.
Answer:
(iii) Bulgaria (C)
(iv) Name a member country of EU that join in 1995.
Answer:
(iv) Austria (D)
Question 26.
Look at the cartoon given below and answer the following guestions. (1 + 1 + 2 = 4)
(i) What is the cartoon representing?
Answer:
Representing the methods adopted by industrialised countries.
(ii) Which country’s personnel being shown in the picture?
Answer:
USA’s personnel are being shown in the picture.
(iii) What message does this picture convey?
Answer:
This picture conveys a message that resources are the real strength of a nation and neo-clolonialism plays politics to obtain it.
![]()
Section E (24 Marks)
Question 27.
Discuss the problems involved with the Integration of Princely States. (6)
Or
Discuss the accession of Hyderabad into Indian Union in detail
Answer:
Ttta very first challenge which came immediately after independence was the Integration of ‘Princely States’ into the Indian Union. The Integration process was as usual not smooth and had various difficulties such as:
(i) At the time of independence it was announced by the British that with the end of their rule over India, paramount of the British Crown over princely states would also lapse. As a result British government took the view that all these states were free to join either India or Pakistan or remain independent if they so wished. This was a very serious problem and could threaten the very existence of a united India.
(ii) Another problem arose very soon. First of all, the ruler of Travancore announced that the state had decided to be independent. Then, the Nizam Hyderabad made a similar announcement. In a similar way Nawab of Bhopal was averse to joining Constituent Assembly.
(iii) This response of the rulers of the princely states meant that after independence there was a very real possibility that India would be further divided into a number of small countries. This was a strange situation since Indian independence was aimed at unity, self-determination as well as democracy.
(iv) In most of these princely states, governments were run in a non-democratic manner and the rulers were unwilling to give democratic rights to their populations.
Or
Hyderabad, the largest of the Princely States was surrounded entirely by Indian Territory. Some parts of the old Hyderabad state are today parts of Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. Its ruler carried the title, ‘Nizam’ and he was one of the world’s richest men. The Nizam wanted an independent status for Hyderabad.
He entered into what was called the Standstill Agreement with India in November 1947 for a year while negotiations with the Indian government were going on. In the meantime, a movement of the people of Hyderabad State against the Nizam’s rule gathered force. The peasantry in the Telangana region in particular, was the victim of Nizam’s oppressive rule and rose against him.
The Communists and the Hyderabad Congress were in the forefront of the movement. The Nizam responded by unleashing a para-military force known as the Razakars on the people. The atrocities and communal nature of the Razakars knew no bounds.
They murdered, maimed, raped and looted, targeting particularly the non Muslims. The Central Government had to order the army to tackle the situation. In September 1948, Indian army moved in to control the Nizam’s forces. After a few days of intermittent fighting, the Nizam surrendered. This led to Hyderabad’s accession to India.
Question 28.
What factor distinguished the Soviet economy from that of a capitalist country like the US. (6)
Or
If the Soviet Union had not disintegrated and the world had remained bipolar, how would that situation have affected the world politics?
Answer:
The three factors that distinguished the Soviet economy from that of a capitalist country like the US were as follows
(i) The Soviet Union was a socialist state where the ‘ major means of production and property were owned by the state while in capitalise countries like US property can be private and business can be individual.
(ii) The Soviet economy focused upon equity of wealth and its balanced distribution among the people. Whereas, the capitalise economy of US doesn’t concern about equitable distribution of resources and considers inequality as a major driving force for people to do better.
(iii) Economies like that of the Soviet Union created and ensured employment for the people. On the contrary capitalist economies like the economy of US were not responsible for unemployment of people and did not guarantee employment.
Or
If the Soviet Union had not disintegrated, it would have affected the world politics in the following manner
- The USA would not have become so powerful and its hegemony would not have been established. It would not be interfering in the world affairs more unilaterally.
- The world would have headed towards a Third World War, if there was no disintegration of USSR. The war would have been more devastating and destructive.
- The disintegration of USSR led to the independence of many countries which were part of erstwhile USSR. This would have not been possible without the disintegration.
- After the disintegration of the Soviet Union, USA’s position in the UNO also became very strong. Almost all the decisions in UNO were taken under the influence of USA. This situation could have been different if there was no collapse of USSR.
- Most of the former Soviet Republics which are passing through conflicts and Civil Wars, would not have gone through this agony.
- Accumulation of nuclear weapons would have continued endlessly.
Question 29.
Discuss the functions of any three principal organs of the United Nations in detail. (6)
Or
Outline the evolution of the United Nations since its establishment in 1945. Describe its functioning with the help of its structures and agencies.
Answer:
The United Nations is an international organisation that strives to maintain world peace and ensure security for all mankind. It also strives to foster friendly relations among nations.
Following are the principal organs of the United Nations
- General Assembly
- Security Council
- Secretariat
- Economic and Social Council
- Trusteeship Council
- International Court of Justice
The functions of these principal organs of UN are
General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) is the chief policy making and representative body of the UN.
- It considers and approves the UN budget and establishes the financial assessments of member countries;
- Elect the non-permanent members of the UN Security Council and the members of other UN organs and councils and, on the recommendation of the UNSC, appoint the Secretary-General;
- Consider and make recommendations on the general principles of cooperation for maintaining international security and peace, including disarmament.
Security Council
The primary responsibility of maintaining peace and security in the world lies with the United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
- The UNSC has 15 member states, five of whom are permanent members.
- The 10 non-permanent members are elected by the General Assembly for a term of two years each, on a regional basis.
International Court of Justice
The ICJ is the chief judicial organ of the United Nations.
- To settle in accordance with international law the legal disputes submitted to it by States.
- To give advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by duly authorised international organs and agencies.
Or
The United Nations was established in 1945 after the end of Second World War as a successor to the League of Nations. The United Nations Charter was signed by 51 States for setting up of UN. The basic aim was to achieve what League of Nations was not able to achieve during the two World Wars. The other objectives of the UN are as follows
- Prevention of conflicts and facilitating co-operation among nations.
- To stop conflicts among states resulting into war and if it takes the shape of war, then to limit the effects of war.
- To reduce the reasons of conflict by bringing the countries together for improving social and economic development all over the world.
UN Structures and Agencies
UN includes many different structures for dealing with different issues. The issues relating to war and peace and differences between member states are dealt by discussion in General Assembly as well as in the Security Council.
The other issues such as social and economic are dealt by a number of agencies which include World Health Organisation (WHO)
United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO)
![]()
Question 30.
Analyse any three main causes of unrest in Jammu and Kashmir. (6)
Or
Suggest any three measures which in your opinion, are very effective to strengthen the national integrity and unity of India.
Answer:
Three main causes of unrest in Jammu and Kashmir are
(i) There is a dispute about the status of Kashmir within the Indian Union. Article 370 gives greater autonomy to Jammu and Kasmir compared to ‘ other state of India. State has its own Constitution. The special attention provokes two opposite reactions. Kashmiries, believe that autonomy conferred by Article 370 is not enough. They should be given more autonomy.
(ii) In 1987 Assembly election, the National Conference Congress alliance gained a massive victory and Farooq Abdullah returned as Chief Minister. By 1989, the state had come in grip of a militant movement mobilised around the cause of a separate Kashmir nation by Pakistan. Throughout the period from 1990, Jammu and Kashmir experienced violence at the hands of the insurgents and through army action.
(iii) The presence of three separate social and politial areas, i.e. Jammu, Kashmir and Ladakh demand intra-state autonomy. Some people within the state and the separatists demand for a separate nation that is not part of India.
Or
Three measures which are very effective to strengthen the national integrity and unity of India are as follows
(i) Value to Regional Aspirations : Expression of regional issues is not an abnormal phenomenon. A large and diverse democracy like India must deal with regional aspirations on a regular basis.
(ii) Democratic Negotiation : The best way to respond to regional aspirations is through democratic negotiations rather than through suppression. In 1980, situation in Punjab, Kashmir and Assam was severely tensed.
Instead of treating these law and order problems, Government of India resolved these through negotiation and discussion.
(iii) Power Sharing among Centre and State : Formal democratic structure is not sufficient. The groups and parties from the regions must be given share in power at the state level. Regions must have share in deciding the destiny of the nation. If they are not given share in the national level decision making, the feeling of injustice and alienation can spread. Regional imbalance in economic development contributes to the feeling of regional discrimination. Regional imbalance is a fact of India’s development experience.
